Protective Effect of Curcumin on CA1 Region of Hippocampus in Rat Model of Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.31661/gmj.v11i.1062Keywords:
Brain Ischemia, Hippocampus, Curcumin, Neuroprotective, ReperfusionAbstract
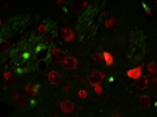
Background: The brain is the most complex and vital organ of the human body. It requires 20-25 % of the total oxygen supply. Because of the limited oxygen and glucose reserves, brain tissue is sensitive to ischemic injury. Indeed, the tolerance of brain tissue for ischemic injury is fragile. Currently, few therapeutic strategies could provide complete neuroprotection. Despite decades of intense research, the beneficial treatment of stroke remains limited. Hence, we aimed to investigate the effect of curcumin on the CA1 region of the hippocampus in a rat model of ischemia/reperfusion (I/R) injury. Materials and Methods: In this experimental research, 24 male Wistar rats were randomly divided into three groups (n=8 per group) as control, I/R, and I/R plus curcumin. All rats underwent bilateral common carotid artery ligation followed by reperfusion. In the treatment group, curcumin (300 mg/kg) was injected 30 minutes before ischemia. Morphological changes of the hippocampus were assessed using Nissl staining, and apoptosis was determined via TUNEL immunohistochemical assays. Results: Nissl staining data showed that the administration of curcumin significantly ameliorated the CA1 pyramidal cell loss due to transient global I/R injury. TUNEL immunohistochemical assays demonstrated that the number of apoptotic cells was significantly lower in the curcumin group than in the I/R groups. Conclusion: Our study demonstrates that curcumin had beneficial activity against ischemia and played a neuroprotective role in the pathogenesis of I/R injury.
References
Liu ZJ, Liu W, Liu L, Xiao C, Wang Y, Jiao JS. Curcumin Protects Neuron against Cerebral Ischemia-Induced Inflammation through Improving PPAR-Gamma Function. Evidence-based Complementary and Alternative Medicine. 2013:470975. https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/470975PMid:23762140 PMCid:PMC3670515 Li L, Li H, Li M. Curcumin protects against cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury by activating JAK2/STAT3 signaling pathway in rats. Int J Clin Exp Med. 2015;8(9):14985-91. Movassaghi S, Sharifi ZN, Soleimani M, Joghataii MT, Hashemi M, Shafaroodi H, et al. Effect of Pentoxifylline on Ischemia- induced Brain Damage and Spatial Memory Impairment in Rat. Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2012;15(5):1083-90. Sharifi ZN, Abolhassani F, Zarrindast MR, Movassaghi S, Rahimian N, Hassanzadeh G. Effects of FK506 on hippocampal CA1 cells following transient global ischemia/reperfusion in Wistar rats. Int J Neurosci. 2012;1(1):1-19. https://doi.org/10.1155/2012/809417PMid:21941688 PMCid:PMC3175409 Faghani M, Ejlali F, Sharifi ZN, Molladoost H, Movassaghi S. The Neuroprotective effect of Atorvastatin on Apoptosis of Hippocampus Following Transient Global Ischemia/Reperfusion. Galen Med J. 2016;5(2):82-9. https://doi.org/10.31661/gmj.v5i2.656 Jangholi E, Sharifi ZN, Hoseinian M, Zarrindast MR, Rahimi HR, Mowla A, et al. Verapamil inhibits mitochondria-induced reactive oxygen species and dependent apoptosis pathways in cerebral transient global ischemia/reperfusion. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2020;2020:5872645. https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/5872645PMid:33133347 PMCid:PMC7591985 Wu J, Li Q, Wang X, Yu S, Li L, Wu X, et al. Neuroprotection by curcumin in ischemic brain injury involves the Akt/Nrf2 pathway. PloS One. 2013;8(3):e59843. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0059843PMid:23555802 PMCid:PMC3610879 Bonfanti R, Musumeci T, Russo C, Pellitteri R. The protective effect of curcumin in Olfactory Ensheathing Cells exposed to hypoxia. Eur J Pharmacol. 2017;796:62-8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejphar.2016.11.038PMid:27889433 Tu XK, Yang WZ, Chen JP, Chen Y, Ouyang LQ, Xu YC, et al. Curcumin inhibits TLR2/4-NF-kappaB signaling pathway and attenuates brain damage in permanent focal cerebral ischemia in rats. Inflamm. 2014;37(5):1544-51. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-014-9881-6PMid:24723245 Wang Q, Sun AY, Simonyi A, Jensen MD, Shelat PB, Rottinghaus GE, et al. Neuroprotective mechanisms of curcumin against cerebral ischemia-induced neuronal apoptosis and behavioral deficits. J Neurosci Res. 2005;82(1):138-48. https://doi.org/10.1002/jnr.20610PMid:16075466 Al-Omar FA, Nagi MN, Abdulgadir MM, Al Joni KS, Al-Majed AA. Immediate and delayed treatments with curcumin prevents forebrain ischemia-induced neuronal damage and oxidative insult in the rat hippocampus. Neurochem Res. 2006;31(5):611-8. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-006-9059-1PMid:16770732 Bokura H, Robinson RG. Long-term cognitive impairment associated with caudate stroke. Stroke. 1997;28(5):970-5. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.STR.28.5.970PMid:9158635 Erfani S, Khaksari M, Oryan S, Shamsaei N, Aboutaleb N, Nikbakht F. Nampt/PBEF/visfatin exerts neuroprotective effects against ischemia/reperfusion injury via modulation of Bax/Bcl-2 ratio and prevention of caspase-3 activation. J Mol Neurosci. 2015;56(1):237-43. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-014-0486-1PMid:25603815 Liu Y, Nakamura T, Toyoshima T, Lu F, Sumitani K, Shinomiya A, et al. Ameliorative effects of yokukansan on behavioral deficits in a gerbil model of global cerebral ischemia. Brain Res. 2014;1543:300-7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainres.2013.11.015PMid:24269335 Kim S, Chin YW, Cho J. Protection of Cultured Cortical Neurons by Luteolin against Oxidative Damage through Inhibition of Apoptosis and Induction of Heme Oxygenase-1. Biol Pharm Bull. 2017;40(3):256-65. https://doi.org/10.1248/bpb.b16-00579PMid:28250268 Kumar KH, Khanum F. Hydroalcoholic extract of cyperus rotundus ameliorates H2O2-induced human neuronal cell damage via its anti-oxidative and anti-apoptotic machinery. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2013;33(1):5-17. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-012-9865-8PMid:22869350 Lakhan SE, Kirchgessner A, Hofer M. Inflammatory mechanisms in ischemic stroke: therapeutic approaches. J Transl Med. 2009;7:97. https://doi.org/10.1186/1479-5876-7-97PMid:19919699 PMCid:PMC2780998 Lim CM, Kim SW, Park JY, Kim C, Yoon SH, Lee JK. Fluoxetine affords robust neuroprotection in the postischemic brain via its anti-inflammatory effect. J Neurosci Res. 2009;87(4):1037-45. https://doi.org/10.1002/jnr.21899PMid:18855941 Zhu H, Fan Y, Sun H, Chen L, Man X. Curcumin inhibits endoplasmic reticulum stress induced by cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats. Exp Med. 2017;14(5):4047-52. https://doi.org/10.3892/etm.2017.5040PMid:29067098 PMCid:PMC5647704 Kunwar A, Barik A, Sandur SK, Indira Priyadarsini K. Differential antioxidant/pro-oxidant activity of dimethoxycurcumin, a synthetic analogue of curcumin. Free Radic Res. 2011;45(8):959-65. https://doi.org/10.3109/10715762.2011.571681PMid:21615275 Gupta SC, Patchva S, Koh W, Aggarwal BB. Discovery of curcumin, a component of golden spice, and its miraculous biological activities. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2012;39(3):283-99. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1440-1681.2011.05648.xPMid:22118895 PMCid:PMC3288651 Thiyagarajan M, Sharma SS. Neuroprotective effect of curcumin in middle cerebral artery occlusion induced focal cerebral ischemia in rats. Life Sci. 2004;74(8):969-85. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lfs.2003.06.042PMid:14672754 Chhunchha B, Fatma N, Kubo E, Rai P, Singh SP, Singh DP. Curcumin abates hypoxia-induced oxidative stress based-ER stress-mediated cell death in mouse hippocampal cells (HT22) by controlling Prdx6 and NF-kappaB regulation. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2013;304(7):C636-55. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpcell.00345.2012PMid:23364261 PMCid:PMC3625714 Feng HL, Dang HZ, Fan H, Chen XP, Rao YX, Ren Y, et al. Curcumin ameliorates insulin signalling pathway in brain of Alzheimer's disease transgenic mice. Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol. 2016;29(4):734-41. https://doi.org/10.1177/0394632016659494PMid:27466310 PMCid:PMC5806850 Jiang TF, Zhang YJ, Zhou HY, Wang HM, Tian LP, Liu J, et al. Curcumin ameliorates the neurodegenerative pathology in A53T alpha-synuclein cell model of Parkinson's disease through the downregulation of mTOR/p70S6K signaling and the recovery of macroautophagy. J Neuroimmune Pharmacol.2013;8(1):356-69. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11481-012-9431-7PMid:23325107 Jiang J, Wang W, Sun YJ, Hu M, Li F, Zhu DY. Neuroprotective effect of curcumin on focal cerebral ischemic rats by preventing blood-brain barrier damage. Eur J Pharmacol. 2007;561(1-3):54-62. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejphar.2006.12.028PMid:17303117 Pan MH, Huang TM, Lin JK. Biotransformation of curcumin through reduction and glucuronidation in mice. Drug Metab Dispos. 1999;27(4):486-94. Zhao J, Zhao Y, Zheng W, Lu Y, Feng G, Yu S. Neuroprotective effect of curcumin on transient focal cerebral ischemia in rats. Brain Res. 2008;1229:224-32. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainres.2008.06.117PMid:18640105 Yu CC, Hu H, Wang XD, Cao H, Ji B, Li J. Effect of curcumin on the injury in hippocampal neurons and the expression of RANTES in hippocamp during cerebral ischemia/ reperfusion in spontaneously hypertensive rats SHR. Chin J Appl Physiol. 2014;30(4):360-4. Huang S, Wang B, Zhang ZQ, Meng ZY, Cao H, Lian QQ, et al. Effect of curcumin on the expression of high mobility group box 1 and apoptotic neurons in hippocampus after global cerebral ischemia reperfusion in rats. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2011;91(19):1340-3. Ye KP, Chen CR, Zheng JW, Cao H, Ji B, Zhou R, et al. Effect of curcumine on the nuclear pathway of JNK dur-ing hippocampal ischemia/reperfusion injury in SHR. Chin J Appl Physiol. 2010;26(4):416-20.