Effects of Titanium Dioxide Nanoparticles and Coenzyme Q10 on Testicular Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury: Role of the Mitochondrial Apoptosis Pathway
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.31661/gmj.v11i.2334Keywords:
Testis, miR-21, circRNA001518, Coenzyme Q10, Titanium Dioxide NanoparticlesAbstract
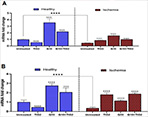
Background: Testicular ischemia-reperfusion (I/R) injury is a urological emergency that can lead to male infertility. So far, no suitable treatment has been found for it. Therefore, in the present study, we investigate the therapeutic effects of concomitant administration of coenzyme Q10 (CoQ10) and titanium dioxide nanoparticles (TiO2-NPs) on testicular I/R damage in rats and the expressions of genes involved in mitochondrial apoptosis, miR-21, and circRNA0001518. Materials and Methods: In this study, after induction of testicular torsion/detorsion, CoQ10 and TiO2-NPs were administered to the rats for ten days. Then, sperm extracted from the epididymides were analyzed for concentration, viability, morphology, and motility. The amount of apoptosis in testicular cells was studied by flow cytometry. Also, the expressions of the Bax and Bcl-2 genes, as well as miR-21 and circRNA0001518 levels were evaluated. Results: Sperm parameters improved in the rats’ testicular that received CoQ10. Administration of TiO2-NPs to healthy rats increased apoptosis and the Bax/Bcl-2 expression ratio. However, its administration to testicular I/R rats alone or in combination with CoQ10 caused a decrease in apoptosis, the Bax/Bcl-2 expression ratio, and an increase in miR-21 and circRNA0001518 expressions. Conclusion: Overall, individual or joint administration of TiO2-NPs or CoQ10 can have therapeutic effects on testicular I/R by altering the expressions of genes in the mitochondrial apoptotic pathway and their regulatory elements.
References
Sha J, Zhou Z, Li J, Yin L, Yang H, Hu G, et al. Spermatogenesis study group. Identification of testis development and spermatogenesis-related genes in human and mouse testes using cDNA arrays. Mol Hum Reprod. 2002;8(6):511-7. https://doi.org/10.1093/molehr/8.6.511PMid:12029067 Omotehara T, Wu X, Kuramasu M, Itoh M. Connection between seminiferous tubules and epididymal duct is originally induced before sex differentiation in a sex-independent manner. Dev Dyn. 2020;249(6):754-64. https://doi.org/10.1002/dvdy.155PMid:32020708 Darsini N, Hamidah B, Suyono SS, Ashari FY, Aswin RH, Yudiwati R. Human Sperm Motility, Viability, and Morphology Decreased after Cryopreservation. Folia Medica Indonesiana. 2019;55(3):198-201. https://doi.org/10.20473/fmi.v55i3.15501 Paul C, Teng S, Saunders PT. A single, mild, transient scrotal heat stress causes hypoxia and oxidative stress in mouse testes, which induces germ cell death. Biol Reprod. 2009;80(5):913-9. https://doi.org/10.1095/biolreprod.108.071779PMid:19144962 PMCid:PMC2709966 Farias JG, Puebla M, Acevedo A, Tapia PJ, Gutierrez E, Zepeda A, et al. Oxidative stress in rat testis and epididymis under intermittent hypobaric hypoxia: protective role of ascorbate supplementation. J Androl. 2010;31(3):314-21. https://doi.org/10.2164/jandrol.108.007054PMid:20378932 Aitken RJ. Reactive oxygen species as mediators of sperm capacitation and pathological damage. Mol Reprod Dev. 2017;84(10):1039-52. https://doi.org/10.1002/mrd.22871PMid:28749007 Arena S, Iacona R, Antonuccio P, Russo T, Salvo V, Gitto E, et al. Medical perspective in testicular ischemia-reperfusion injury. Exp Ther Med. 2017;13(5):2115-22. https://doi.org/10.3892/etm.2017.4289PMid:28565817 PMCid:PMC5443302 Tuglu D, Yuvanc E, Yilmaz E, Gencay IY, Atasoy P, Kisa U, et al. The antioxidant effect of dexmedetomidine on testicular ischemia-reperfusion injury. Acta Cir Bras. 2015;30(6):414-21. https://doi.org/10.1590/S0102-865020150060000007PMid:26108030 Al Saadi T, Assaf Y, Farwati M, Turkmani K, Al-Mouakeh A, Shebli B, et al. Coenzyme Q10 for heart failure. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021;2(2):CD008684. https://doi.org/10.1002/14651858.CD008684.pub3PMid:35608922 PMCid:PMC8092430 Crane FL. Discovery of ubiquinone (coenzyme Q) and an overview of function. Mitochondrion. 2007;7 Suppl:S2-7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mito.2007.02.011PMid:17446142 Prakash S, Sunitha J, Hans M. Role of coenzyme Q(10) as an antioxidant and bioenergizer in periodontal diseases. Indian J Pharmacol. 2010;42(6):334-7. https://doi.org/10.4103/0253-7613.71884PMid:21189900 PMCid:PMC2991687 Hussain M, Ceccarelli R, Marchisio D, Fino D, Russo N, Geobaldo F. Synthesis, characterization, and photocatalytic application of novel TiO2 nanoparticles. CEJ. 2010;157(1):45-51. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2009.10.043 Hirst SM, Karakoti A, Singh S, Self W, Tyler R, Seal S, et al. Bio-distribution and in vivo antioxidant effects of cerium oxide nanoparticles in mice. Environ Toxicol. 2013;28(2):107-18. https://doi.org/10.1002/tox.20704PMid:21618676 Eriksson P, Tal AA, Skallberg A, Brommesson C, Hu Z, Boyd RD, et al. Cerium oxide nanoparticles with antioxidant capabilities and gadolinium integration for MRI contrast enhancement. Sci Rep. 2018;8(1):6999. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-25390-zPMid:29725117 PMCid:PMC5934375 Abdelazim AM, Saadeldin IM, Swelum AA, Afifi MM, Alkaladi A. Oxidative Stress in the Muscles of the Fish Nile Tilapia Caused by Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles and Its Modulation by Vitamins C and E. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2018;2018:6926712. https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/6926712PMid:29849910 PMCid:PMC5907420 Liu KS, Pan F, Mao XD, Liu C, Chen YJ. Biological functions of circular RNAs and their roles in occurrence of reproduction and gynecological diseases. Am J Transl Res. 2019;11(1):1-15. Elshaari F, Elfageih R, Sheriff D. Testicular Torsion-Detorsion- Histological and Biochemical Changes in Rat Testis. J Cytol Histol. 2012;3:136. Entezari M, Sharifi ZN, Movassaghi S, Atabi F, Jamali Z, Salimi A. Neuroprotective Effects of Cyperus rotundus Rhizome Extract on Ischemic Brain Injury: Expression profile of Bax, Bcl2, Bad and Bclxl Genes. Drug & Advanced Sciences Journal. 2019;1(1):25-30. Xu X, Kriegel AJ, Jiao X, Liu H, Bai X, Olson J, et al. miR-21 in ischemia/reperfusion injury: a double-edged sword? Physiol Genomics. 2014;46(21):789-97. https://doi.org/10.1152/physiolgenomics.00020.2014PMid:25159851 PMCid:PMC4280148 Wilhelm Filho D, Torres MA, Bordin AL, Crezcynski-Pasa TB, Boveris A. Spermatic cord torsion, reactive oxygen and nitrogen species and ischemia-reperfusion injury. Mol Aspects Med. 2004;25(1-2):199-210. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mam.2004.02.020PMid:15051328 Dokmeci D. Testicular torsion, oxidative stress and the role of antioxidant therapy. Folia Med (Plovdiv). 2006;48(3-4):16-21. Mancini A, Balercia G. Coenzyme Q(10) in male infertility: physiopathology and therapy. Biofactors. 2011;37(5):374-80. https://doi.org/10.1002/biof.164PMid:21989906 Lafuente R, González-Comadrán M, Solà I, López G, Brassesco M, Carreras R, et al. Coenzyme Q10 and male infertility: a meta-analysis. J Assist Reprod Genet. 2013;30(9):1147-56. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10815-013-0047-5PMid:23912751 PMCid:PMC3800531 Iravani S. Green synthesis of metal nanoparticles using plants. Green Chem. 2011;13(10):2638-50. https://doi.org/10.1039/c1gc15386b Pourmorad F, Hosseinimehr S, Shahabimajd N. Antioxidant activity, phenol and flavonoid contents of some selected Iranian medicinal plants. AJB. 2006;5(11):1142-45. Santhoshkumar T, Rahuman AA, Jayaseelan C, Rajakumar G, Marimuthu S, Kirthi AV, et al. Green synthesis of titanium dioxide nanoparticles using Psidium guajava extract and its antibacterial and antioxidant properties. Asian Pac J Trop Med. 2014;7(12):968-76. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1995-7645(14)60171-1PMid:25479626 Dousti B, Nabipour F, Hajiamraei A. Green Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticle Using Aqueous Extract of Fumaria Parviflora and Study of its Antibacterial and Antioxidant Properties. RJMS. 2019;26(6):105-17. Taghizadeh L, Eidi A, Mortazavi P, Rohani AH. Effect of selenium on testicular damage induced by varicocele in adult male Wistar rats. J Trace Elem Med Biol. 2017;44:177-85. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtemb.2017.08.003PMid:28965574 Sedha S, Kumar S, Shukla S. Role of Oxidative Stress in Male Reproductive Dysfunctions with Reference to Phthalate Compounds. Urol J. 2015;12(5):2304-16. Agarwal A, Sharma RK, Nallella KP, Thomas AJ Jr, Alvarez JG, Sikka SC. Reactive oxygen species as an independent marker of male factor infertility. Fertil Steril. 2006;86(4):878-85. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fertnstert.2006.02.111PMid:17027357 Cheng EH, Kirsch DG, Clem RJ, Ravi R, Kastan MB, Bedi A, et al. Conversion of Bcl-2 to a Bax-like death effector by caspases. Science. 1997;278(5345):1966-8. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.278.5345.1966PMid:9395403 Kowaltowski AJ, Vercesi AE, Fiskum G. Bcl-2 prevents mitochondrial permeability transition and cytochrome c release via maintenance of reduced pyridine nucleotides. Cell Death Differ. 2000;7(10):903-10. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.cdd.4400722PMid:11279535 Yang J, Liu X, Bhalla K, Kim CN, Ibrado AM, Cai J, et al. Prevention of apoptosis by Bcl-2: release of cytochrome c from mitochondria blocked. Science. 1997; 275(5303):1129-32. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.275.5303.1129PMid:9027314 Murphy KM, Ranganathan V, Farnsworth ML, Kavallaris M, Lock RB. Bcl-2 inhibits Bax translocation from cytosol to mitochondria during drug-induced apoptosis of human tumor cells. Cell Death Differ. 2000;7(1):102-11. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.cdd.4400597PMid:10713725 Shahrooz R, Moloody-Tappe M, Razi M, Zarei L, Mohammadi V. Investigation of the Effect of Coenzyme Q10 Supplementation on Apoptosis Gene Expression and Oxidative Stress after Busulfan Injection in Rats. Yafte. 2020;21(4):118-30. El-Khadragy M, Al-Megrin WA, AlSadhan NA, Metwally DM, El-Hennamy RE, Salem FEH, et al. Impact of Coenzyme Q10 Administration on Lead Acetate-Induced Testicular Damage in Rats. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2020;2020:4981386. https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/4981386PMid:32566085 PMCid:PMC7290879 Wang Y, Zhou S, Fan K, Jiang C. MicroRNA-21 and its impact on signaling pathways in cervical cancer. Oncol Lett. 2019;17(3):3066-70. https://doi.org/10.3892/ol.2019.10002PMid:30867735 PMCid:PMC6396207 Zare Z, Eimani H, Mohammadi M, Mofid M, Dashtnavard H. The effect of orally administered L-carnitine on testis tissue, sperm parameters and daily sperm production in adult mice. Yakhteh. 2010;11(4):382-9. Zhong Y, Du Y, Yang X, Mo Y, Fan C, Xiong F, et al. Circular RNAs function as ceRNAs to regulate and control human cancer progression. Mol Cancer. 2018;17(1):79. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-018-0827-8PMid:29626935 PMCid:PMC5889847 Abi A, Farahani N, Molavi G, Gheibi Hayat SM. Circular RNAs: epigenetic regulators in cancerous and noncancerous skin diseases. Cancer Gene Ther. 2020;27(5):280-93. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41417-019-0130-xPMid:31477805 Ikebuaso AD, Yama OE, Duru FI, Oyebadejo SA. Experimental Testicular Torsion in a Rat Model: Effects of Treatment with Pausinystalia macroceras on Testis Functions. J Reprod Infertil. 2012;13(4):218-24 Zang J, Lu D, Xu A. The interaction of circRNAs and RNA binding proteins: An important part of circRNA maintenance and function. J Neurosci Res. 2020;98(1):87-97. https://doi.org/10.1002/jnr.24356PMid:30575990 Wang H, Zhou W, Zhang J, Li H. Role of JNK and ERK1/2 MAPK signaling pathway in testicular injury of rats induced by di-N-butyl-phthalate (DBP). Biol Res. 2019;52(1):41. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40659-019-0248-1PMid:31387634 PMCid:PMC6685163