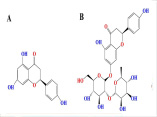
Neuropharmaceutical Properties of Naringin Against Alzheimer's and Parkinson's Diseases
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.31661/gmj.v11i.2337Keywords:
Flavonoids, Parkinson's Disease, Naringenin, Naringin, Alzheimer's Disease, Neurological DisorderAbstract
Neurological complications are considered the leading cause of disability and the second cause of death worldwide. Although the most common neurological disorders affecting a large population are Alzheimer's (AD) and Parkinson's diseases (PD), no definitive treatment has been propounded in the clinic. As in recent years, special attention has been paid to medicinal herbal products as one of the ways to meet the challenges of treating diseases. This review study aimed to introduce the naringin neuroprotective effects as an abundant flavonoid in grapes and citrus fruits on the most common neurological disorders, including AD and PD. For this purpose, the specified keywords were searched in PubMed, Web of Science, Scopus, Embase, and Google Scholar, and the results were entered into the study after a concise overview. The findings show naringin can confront neurological disorders through several mechanisms such as modulating stress response pathways, preventing apoptosis, oxidative stress, and neuroinflammation, excessive chelating amounts of metal ions, thereby improving cognitive impairment and memory loss induced by neurological disorders. However, further studies, particularly on human, are critical for the final confirmation of obtained findings.
References
Feigin VL, Nichols E, Alam T, Bannick MS, Beghi E, Blake N, et al. Global, regional, and national burden of neurological disorders, 1990-2016: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2016. Lancet Neurol. 2019;18(5):459-80. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1474-4422(18)30499-X Deverman BE, Ravina BM, Bankiewicz KS, Paul SM, Sah DWY. Gene therapy for neurological disorders: progress and prospects. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2018;17(9):641-59. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrd.2018.110PMid:30093643 Espay AJ, Aybek S, Carson A, Edwards MJ, Goldstein LH, Hallett M, et al. Current Concepts in Diagnosis and Treatment of Functional Neurological Disorders. JAMA Neurol. 2018;75(9):1132-41. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamaneurol.2018.1264PMid:29868890 PMCid:PMC7293766 Lee J, Jin C, Cho SY, Park SU, Jung WS, Moon SK, Park JM, Ko CN, Cho KH, Kwon S. Herbal medicine treatment for Alzheimer disease: A protocol for a systematic review and meta-analysis. Medicine (Baltimore). 2020;99(33):e21745. https://doi.org/10.1097/MD.0000000000021745PMid:32872063 PMCid:PMC7437827 Liang YT, Lin CY, Wang YH, Chou HH, Wei JC. Associations of Chinese Herbal Medicine Usage with Risk of Dementia in Patients with Parkinson's Disease: A Population-Based, Nested Case-Control Study. J Altern Complement Med. 2021;27(7):606-12. https://doi.org/10.1089/acm.2020.0422PMid:33979532 Memariani Z, Abbas SQ, Ul Hassan SS, Ahmadi A, Chabra A. Naringin and naringenin as anticancer agents and adjuvants in cancer combination therapy: Efficacy and molecular mechanisms of action, a comprehensive narrative review. Pharmacol Res. 2021;171:105264. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phrs.2020.105264PMid:33166734 Samare-Najaf M, Samareh A, Jamali N, Abbasi A, Clark CC, Khorchani MJ, Zal F. Adverse Effects and Safety of Etirinotecan Pegol, a Novel Topoisomerase Inhibitor, in Cancer Treatment: A Systematic Review. Curr Cancer Ther Rev. 2021;17(3):234-43. https://doi.org/10.2174/1573394717666210202103502 Samare-Najaf M, Zal F, Safari S, Koohpeyma F, Jamali N. Stereological and histopathological evaluation of doxorubicin-induced toxicity in female rats' ovary and uterus and palliative effects of quercetin and vitamin E. Hum Exp Toxicol. 2020;39(12):1710-24. https://doi.org/10.1177/0960327120937329PMid:32666839 Rostami S, Azhdarpoor A, Baghapour MA, Dehghani M, Samaei MR, Jaskulak M, et al. The effects of exogenous application of melatonin on the degradation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in the rhizosphere of Festuca. Environ Pollut. 2021;274:116559. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2021.116559PMid:33529892 Jamali N, Zal F, Mostafavi-Pour Z, Samare-Najaf M, Poordast T, Dehghanian A. Ameliorative Effects of Quercetin and Metformin and Their Combination Against Experimental Endometriosis in Rats. Reprod Sci. 2021;28(3):683-92. https://doi.org/10.1007/s43032-020-00377-2PMid:33141412 Samare-Najaf M, Zal F, Safari S. Primary and Secondary Markers of Doxorubicin-Induced Female Infertility and the Alleviative Properties of Quercetin and Vitamin E in a Rat Model. Reprod Toxicol. 2020 S;96:316-26. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.reprotox.2020.07.015PMid:32810592 Jamali N, Jalali M, Saffari-Chaleshtori J, Samare-Najaf M, Samareh A. Effect of cinnamon supplementation on blood pressure and anthropometric parameters in patients with type 2 diabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis of clinical trials. Diabetes Metab Syndr. 2020;14(2):119-25. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dsx.2020.01.009PMid:32032898 Jamali N, Kazemi A, Saffari-Chaleshtori J, Samare-Najaf M, Mohammadi V, Clark CCT. The effect of cinnamon supplementation on lipid profiles in patients with type 2 diabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis of clinical trials. Complement Ther Med. 2020;55:102571. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ctim.2020.102571PMid:33220625 Li S, Jiang J, Fang J, Li X, Huang C, Liang W, Wu K. Naringin protects H9C2 cardiomyocytes from chemical hypoxia induced injury by promoting the autophagic flux via the activation of the HIF 1α/BNIP3 signaling pathway. Int J Mol Med. 2021;47(6):102. https://doi.org/10.3892/ijmm.2021.4935PMid:33907819 Jamali N, Soureshjani EH, Mobini GR, Samare-Najaf M, Clark CCT, Saffari-Chaleshtori J. Medicinal plant compounds as promising inhibitors of coronavirus (COVID-19) main protease: an in silico study. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 2021:1-12. https://doi.org/10.1080/07391102.2021.1906749PMid:33970805 Benameur T, Soleti R, Porro C. The Potential Neuroprotective Role of Free and Encapsulated Quercetin Mediated by miRNA against Neurological Diseases. Nutrients. 2021;13(4):1318. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13041318PMid:33923599 PMCid:PMC8073422 Aihaiti Y, Song Cai Y, Tuerhong X, Ni Yang Y, Ma Y, Shi Zheng H, Xu K, Xu P. Therapeutic Effects of Naringin in Rheumatoid Arthritis: Network Pharmacology and Experimental Validation. Front Pharmacol. 2021;12:672054. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2021.672054PMid:34054546 PMCid:PMC8160516 Benavente-GarcÃa O, Castillo J. Update on uses and properties of citrus flavonoids: new findings in anticancer, cardiovascular, and anti-inflammatory activity. J Agric Food Chem. 2008;56(15):6185-205. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf8006568PMid:18593176 Yonekura-Sakakibara K, Higashi Y, Nakabayashi R. The Origin and Evolution of Plant Flavonoid Metabolism. Front Plant Sci. 2019;10:943. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2019.00943PMid:31428108 PMCid:PMC6688129 Cavia-Saiz M, Busto MD, Pilar-Izquierdo MC, Ortega N, Perez-Mateos M, Muñiz P. Antioxidant properties, radical scavenging activity and biomolecule protection capacity of flavonoid naringenin and its glycoside naringin: a comparative study. J Sci Food Agric. 2010;90(7):1238-44. https://doi.org/10.1002/jsfa.3959PMid:20394007 Jucá MM, Cysne Filho FMS, De Almeida JC, Mesquita DDS, Barriga JRM, Dias KCF, et al. Flavonoids: biological activities and therapeutic potential. Nat Prod Res. 2020;34(5):692-705. https://doi.org/10.1080/14786419.2018.1493588PMid:30445839 Chen YC, Shen SC, Lin HY. Rutinoside at C7 attenuates the apoptosis-inducing activity of flavonoids. Biochem Pharmacol. 2003;66(7):1139-50. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0006-2952(03)00455-6 Chen R, Qi QL, Wang MT, Li QY. Therapeutic potential of naringin: an overview. Pharm Biol. 2016;54(12):3203-10. https://doi.org/10.1080/13880209.2016.1216131PMid:27564838 Lather A, Sharma S, Khatkar A. Naringin derivatives as glucosamine-6-phosphate synthase inhibitors based preservatives and their biological evaluation. Sci Rep. 2020;10(1):20477. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-77511-2PMid:33235242 PMCid:PMC7686335 ÅžekeroÄŸlu G, FadıloÄŸlu S, Göğüş F. Immobilization and characterization of naringinase for the hydrolysis of naringin. Eur Food Res Technol. 2006;224(1):55-60. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00217-006-0288-y Wang J, Ye X, Lin S, Liu H, Qiang Y, Chen H, Jiang Z, et al. Preparation, characterization and in vitro and in vivo evaluation of a solid dispersion of Naringin. Drug Dev Ind Pharm. 2018;44(11):1725-32. https://doi.org/10.1080/03639045.2018.1483390PMid:29851514 Gelen V, Åžengül E. Antioxidant, anti-inflammatory and antiapoptotic effects of Naringin on cardiac damage induced by cisplatin. Indian J Tradit Know. 2020;19(2):459-65. https://doi.org/10.56042/ijtk.v19i2.35371 Hussain K, Ali I, Ullah S, Imran M, Parveen S, Kanwal T, et al. Enhanced antibacterial potential of naringin loaded β cyclodextrin nanoparticles. J Clust Sci. 2022;33(1):339-48. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10876-020-01972-8 Li P, Wang S, Guan X, Cen X, Hu C, Peng W, Wang Y, Su W. Six months chronic toxicological evaluation of naringin in Sprague-Dawley rats. Food Chem Toxicol. 2014;66:65-75. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fct.2014.01.023PMid:24462649 Akamo AJ, Rotimi SO, Akinloye DI, Ugbaja RN, Adeleye OO, Dosumu OA, et al. Naringin prevents cyclophosphamide-induced hepatotoxicity in rats by attenuating oxidative stress, fibrosis, and inflammation. Food Chem Toxicol. 2021;153:112266. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fct.2021.112266PMid:33992719 Ge X, Zhou G. Protective effects of naringin on glucocorticoid-induced osteoporosis through regulating the PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway. Am J Transl Res. 2021;13(6):6330-41. Syed AA, Reza MI, Shafiq M, Kumariya S, Singh P, Husain A, et al. Naringin ameliorates type 2 diabetes mellitus-induced steatohepatitis by inhibiting RAGE/NF-κB mediated mitochondrial apoptosis. Life Sci. 2020;257:118118. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lfs.2020.118118PMid:32702445 Zhao Y, Liu S. Bioactivity of naringin and related mechanisms. Pharmazie. 2021;76(8):359-63. Lutz MW, Sprague D, Barrera J, Chiba-Falek O. Shared genetic etiology underlying Alzheimer's disease and major depressive disorder. Transl Psychiatry. 2020;10(1):88. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41398-020-0769-yPMid:32152295 PMCid:PMC7062839 Sachdeva AK, Kuhad A, Chopra K. Naringin ameliorates memory deficits in experimental paradigm of Alzheimer's disease by attenuating mitochondrial dysfunction. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2014;127:101-10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pbb.2014.11.002PMid:25449356 Thomas GEC, Leyland LA, Schrag AE, Lees AJ, Acosta-Cabronero J, Weil RS. Brain iron deposition is linked with cognitive severity in Parkinson's disease. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2020;91(4):418-25. https://doi.org/10.1136/jnnp-2019-322042PMid:32079673 PMCid:PMC7147185 Wang DM, Yang YJ, Zhang L, Zhang X, Guan FF, Zhang LF. Naringin Enhances CaMKII Activity and Improves Long-Term Memory in a Mouse Model of Alzheimer's Disease. Int J Mol Sci. 2013;14(3):5576-86. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms14035576PMid:23478434 PMCid:PMC3634479 Kumar A, Dogra S, Prakash A. Protective effect of naringin, a citrus flavonoid, against colchicine-induced cognitive dysfunction and oxidative damage in rats. J Med Food. 2010;13(4):976-84. https://doi.org/10.1089/jmf.2009.1251PMid:20673063 Prabhakar O. Naringin Attenuates Aluminum Induced Cognitive Deficits in Rats. Indian J Pharm Educ Res. 2020;54:674-81. https://doi.org/10.5530/ijper.54.3.117 Ramalingayya GV, Nampoothiri M, Nayak PG, Kishore A, Shenoy RR, Mallikarjuna Rao C, Nandakumar K. Naringin and Rutin Alleviates Episodic Memory Deficits in Two Differentially Challenged Object Recognition Tasks. Pharmacogn Mag. 2016;12(Suppl 1):S63-70. https://doi.org/10.4103/0973-1296.176104PMid:27041861 PMCid:PMC4792002 Wu BW, Guo JD, Wu MS, Liu Y, Lu M, Zhou YH, Han HW. Osteoblast-derived lipocalin-2 regulated by miRNA-96-5p/Foxo1 advances the progression of Alzheimer's disease. Epigenomics. 2020;12(17):1501-13. https://doi.org/10.2217/epi-2019-0215PMid:32901506 Kaur G, Prakash A. Involvement of the nitric oxide signaling in modulation of naringin against intranasal manganese and intracerbroventricular β-amyloid induced neurotoxicity in rats. J Nutr Biochem. 2020;76:108255. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnutbio.2019.108255PMid:31759198 Kumar A, Prakash A, Dogra S. Naringin alleviates cognitive impairment, mitochondrial dysfunction and oxidative stress induced by D-galactose in mice. Food Chem Toxicol. 2010;48(2):626-32. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fct.2009.11.043PMid:19941926 Sachdeva AK, Chopra K. Naringin mitigate okadaic acid-induced cognitive impairment in an experimental paradigm of Alzheimer's disease. J Funct Foods. 2015;19:110-25. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jff.2015.08.024 Wang D, Gao K, Li X, Shen X, Zhang X, Ma C, Qin C, Zhang L. Long-term naringin consumption reverses a glucose uptake defect and improves cognitive deficits in a mouse model of Alzheimer's disease. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2012;102(1):13-20. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pbb.2012.03.013PMid:22741174 Wang DM, Yang YJ, Zhang L, Zhang X, Guan FF, Zhang LF. Naringin Enhances CaMKII Activity and Improves Long-Term Memory in a Mouse Model of Alzheimer's Disease. Int J Mol Sci. 2013;14(3):5576-86. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms14035576PMid:23478434 PMCid:PMC3634479 Yang W, Zhou K, Zhou Y, An Y, Hu T, Lu J, Huang S, Pei G. Naringin Dihydrochalcone Ameliorates Cognitive Deficits and Neuropathology in APP/PS1 Transgenic Mice. Front Aging Neurosci. 2018;10:169. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnagi.2018.00169PMid:29922152 PMCid:PMC5996202 Meng X, Fu M, Wang S, Chen W, Wang J, Zhang N. Naringin ameliorates memory deficits and exerts neuroprotective effects in a mouse model of Alzheimer's disease by regulating multiple metabolic pathways. Mol Med Rep. 2021;23(5):332. https://doi.org/10.3892/mmr.2021.11971PMid:33760152 PMCid:PMC7974313 Estevez AO, Morgan KL, Szewczyk NJ, Gems D, Estevez M. The neurodegenerative effects of selenium are inhibited by FOXO and PINK1/PTEN regulation of insulin/insulin-like growth factor signaling in Caenorhabditis elegans. Neurotoxicology. 2014;41(100):28-43. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuro.2013.12.012PMid:24406377 PMCid:PMC3979119 Zhao Y, Yang J, Liao W, Liu X, Zhang H, Wang S, Wang D, Feng J, Yu L, Zhu WG. Cytosolic FoxO1 is essential for the induction of autophagy and tumour suppressor activity. Nat Cell Biol. 2010;12(7):665-75. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncb2069PMid:20543840 Jiang X, Niu X, Guo Q, Dong Y, Xu J, Yin N, et al. FoxO1-mediated autophagy plays an important role in the neuroprotective effects of hydrogen in a rat model of vascular dementia. Behav Brain Res. 2019;356:98-106. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbr.2018.05.023PMid:29885845 Kimura A, Hata S, Suzuki T. Alternative Selection of β-Site APP-Cleaving Enzyme 1 (BACE1) Cleavage Sites in Amyloid β-Protein Precursor (APP) Harboring Protective and Pathogenic Mutations within the Aβ Sequence. J Biol Chem. 2016;291(46):24041-53. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M116.744722PMid:27687728 PMCid:PMC5104930 Hampel H, Blennow K, Shaw LM, Hoessler YC, Zetterberg H, Trojanowski JQ. Total and phosphorylated tau protein as biological markers of Alzheimer's disease. Exp Gerontol. 2010;45(1):30-40. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.exger.2009.10.010PMid:19853650 PMCid:PMC2815003 Saito T, Oba T, Shimizu S, Asada A, Iijima KM, Ando K. Cdk5 increases MARK4 activity and augments pathological tau accumulation and toxicity through tau phosphorylation at Ser262. Hum Mol Genet. 2019;28(18):3062-71. https://doi.org/10.1093/hmg/ddz120PMid:31174206 Rabbito A, Dulewicz M, KulczyÅ„ska-Przybik A, Mroczko B. Biochemical Markers in Alzheimer's Disease. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(6):1989. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21061989PMid:32183332 PMCid:PMC7139967 Ben-Shushan S, Miller Y. Neuropeptides: Roles and Activities as Metal Chelators in Neurodegenerative Diseases. J Phys Chem B. 2021;125(11):2796-811. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jpcb.0c11151PMid:33570949 PMCid:PMC8389909 Ferreira-Vieira TH, Guimaraes IM, Silva FR, Ribeiro FM. Alzheimer's disease: Targeting the Cholinergic System. Curr Neuropharmacol. 2016;14(1):101-15. https://doi.org/10.2174/1570159X13666150716165726PMid:26813123 PMCid:PMC4787279 Ahmad SS, Akhtar S, Jamal QM, Rizvi SM, Kamal MA, Khan MK, Siddiqui MH. Multiple Targets for the Management of Alzheimer's Disease. CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets. 2016;15(10):1279-89. https://doi.org/10.2174/1871527315666161003165855PMid:27712576 Liu MY, Zeng F, Shen Y, Wang YY, Zhang N, Geng F. Bioguided Isolation and Structure Identification of Acetylcholinesterase Enzyme Inhibitors from Drynariae Rhizome. J Anal Methods Chem. 2020;2020:2971841. https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/2971841PMid:32185082 PMCid:PMC7059089 Mani VM, Asha S, Sadiq AM. Pyrethroid deltamethrin-induced developmental neurodegenerative cerebral injury and ameliorating effect of dietary glycoside naringin in male wistar rats. Biomed Aging Pathol. 2014;4(1):1-8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biomag.2013.11.001 Orhan I, Kartal M, Tosun F, Sener B. Screening of various phenolic acids and flavonoid derivatives for their anticholinesterase potential. Z Naturforsch C J Biosci. 2007;62(11-12):829-32. https://doi.org/10.1515/znc-2007-11-1210PMid:18274286 Heneka MT, Carson MJ, El Khoury J, Landreth GE, Brosseron F, Feinstein DL, Jacobs AH, Wyss-Coray T, Vitorica J, Ransohoff RM, Herrup K. Neuroinflammation in Alzheimer's disease. Lancet Neurol. 2015;14(4):388-405. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1474-4422(15)70016-5 McGeer EG, McGeer PL. Inflammatory processes in Alzheimer's disease. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2003;27(5):741-9. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0278-5846(03)00124-6 Burke RE, O'Malley K. Axon degeneration in Parkinson's disease. Exp Neurol. 2013;246:72-83. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.expneurol.2012.01.011PMid:22285449 PMCid:PMC3340476 Geibl FF, Henrich MT, Oertel WH. Mesencephalic and extramesencephalic dopaminergic systems in Parkinson's disease. J Neural Transm (Vienna). 2019;126(4):377-96. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00702-019-01970-9PMid:30643975 Darbinyan LV, Hambardzumyan LE, Simonyan KV, Chavushyan VA, Manukyan LP, Badalyan SA, et al. Protective effects of curcumin against rotenone-induced rat model of Parkinson's disease: in vivo electrophysiological and behavioral study. Metab Brain Dis. 2017;32(6):1791-803. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-017-0060-yPMid:28695411 Islam MS, Quispe C, Hossain R, Islam MT, Al-Harrasi A, Al-Rawahi A, Martorell M, Mamurova A, Seilkhan A, Altybaeva N, Abdullayeva B, Docea AO, Calina D, Sharifi-Rad J. Neuropharmacological Effects of Quercetin: A Literature-Based Review. Front Pharmacol. 2021;12:665031. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2021.665031PMid:34220504 PMCid:PMC8248808 Prasad EM, Hung SY. Behavioral Tests in Neurotoxin-Induced Animal Models of Parkinson's Disease. Antioxidants (Basel). 2020;9(10):1007. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox9101007PMid:33081318 PMCid:PMC7602991 Su CF, Jiang L, Zhang XW, Iyaswamy A, Li M. Resveratrol in Rodent Models of Parkinson's Disease: A Systematic Review of Experimental Studies. Front Pharmacol. 2021;12:644219. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2021.644219PMid:33967780 PMCid:PMC8100515 Ay M, Luo J, Langley M, Jin H, Anantharam V, Kanthasamy A, et al. Molecular mechanisms underlying protective effects of quercetin against mitochondrial dysfunction and progressive dopaminergic neurodegeneration in cell culture and MitoPark transgenic mouse models of Parkinson's Disease. J Neurochem. 2017;141(5):766-82. https://doi.org/10.1111/jnc.14033PMid:28376279 PMCid:PMC5643047 Panneton WM, Kumar VB, Gan Q, Burke WJ, Galvin JE. The neurotoxicity of DOPAL: behavioral and stereological evidence for its role in Parkinson disease pathogenesis. PLoS One. 2010;5(12):e15251. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0015251PMid:21179455 PMCid:PMC3001493 Rasheed MSU, Tripathi MK, Patel DK, Singh MP. Resveratrol Regulates Nrf2-Mediated Expression of Antioxidant and Xenobiotic Metabolizing Enzymes in Pesticides-Induced Parkinsonism. Protein Pept Lett. 2020;27(10):1038-45. https://doi.org/10.2174/0929866527666200403110036PMid:32242774 Sharma S, Raj K, Singh S. Neuroprotective Effect of Quercetin in Combination with Piperine Against Rotenone- and Iron Supplement-Induced Parkinson's Disease in Experimental Rats. Neurotox Res. 2020;37(1):198-209. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12640-019-00120-zPMid:31654381 Garabadu D, Agrawal N. Naringin Exhibits Neuroprotection Against Rotenone-Induced Neurotoxicity in Experimental Rodents. Neuromolecular Med. 2020;22(2):314-30. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12017-019-08590-2PMid:31916219 Medeiros-Linard CFB, Andrade-da-Costa BLDS, Augusto RL, Sereniki A, Trevisan MTS, Perreira RCR, et al. Anacardic Acids from Cashew Nuts Prevent Behavioral Changes and Oxidative Stress Induced by Rotenone in a Rat Model of Parkinson's Disease. Neurotox Res. 2018;34(2):250-62. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12640-018-9882-6PMid:29520721 Fouzder C, Mukhuty A, Mukherjee S, Malick C, Kundu R. Trigonelline inhibits Nrf2 via EGFR signalling pathway and augments efficacy of Cisplatin and Etoposide in NSCLC cells. Toxicol In Vitro. 202;70:105038. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tiv.2020.105038PMid:33148531 Clerici S, Boletta A. Role of the KEAP1-NRF2 Axis in Renal Cell Carcinoma. Cancers (Basel). 2020;12(11):3458. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12113458PMid:33233657 PMCid:PMC7699726 Tao J, Krutsenko Y, Moghe A, Singh S, Poddar M, Bell A, et al. Nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 and β-Catenin Coactivation in Hepatocellular Cancer: Biological and Therapeutic Implications. Hepatology. 2021;74(2):741-59. https://doi.org/10.1002/hep.31730PMid:33529367 PMCid:PMC8326305 Kim HD, Jeong KH, Jung UJ, Kim SR. Naringin treatment induces neuroprotective effects in a mouse model of Parkinson's disease in vivo, but not enough to restore the lesioned dopaminergic system. J Nutr Biochem. 2016;28:140-6. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnutbio.2015.10.013PMid:26878791 Urrutia PJ, Mena NP, Núñez MT. The interplay between iron accumulation, mitochondrial dysfunction, and inflammation during the execution step of neurodegenerative disorders. Front Pharmacol. 2014;5:38. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2014.00038PMid:24653700 PMCid:PMC3948003 Leem E, Nam JH, Jeon MT, Shin WH, Won SY, Park SJ, Choi MS, Jin BK, Jung UJ, Kim SR. Naringin protects the nigrostriatal dopaminergic projection through induction of GDNF in a neurotoxin model of Parkinson's disease. J Nutr Biochem. 2014;25(7):801-6. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnutbio.2014.03.006PMid:24797334 Gentile G, La Cognata V, Cavallaro S. The contribution of CNVs to the most common aging-related neurodegenerative diseases. Aging Clin Exp Res. 2021;33(5):1187-95. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40520-020-01485-4PMid:32026430 Zhu Q, Qu Y, Zhou XG, Chen JN, Luo HR, Wu GS. A Dihydroflavonoid Naringin Extends the Lifespan of C. elegans and Delays the Progression of Aging-Related Diseases in PD/AD Models via DAF-16. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2020;2020:6069354. https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/6069354PMid:32832002 PMCid:PMC7422489