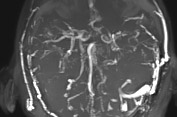
Cerebral venous sinus thrombosis
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.31661/gmj.v5i.594Abstract
Cerebral venous thrombosis (CVT) is occlusion of dural sinuses and/or cortical veins due to clot formation. It is a potentially  life-threatening condition that requires rapid diagnosis and urgent treatment.
Cerebral venous thrombosis is   more common in  females and young people. Pregnancy, postpartum state, contraceptive pills, infection, malignancy,  hyper-coagulable state, rheumatological disorders, trauma are among the major etiologies of cerebral venous thrombosis. Headache, focal neurologic deficits and seizure were the most common clinical presentations. Different techniques of unenhanced and contrast enhanced   brain computerized tomography(CT scan) and ,magnetic resonance imaging(MRI) are the most helpful ancillary investigations for diagnosis of Cerebral venous thrombosis.
Specific treatment  of the underlying cause of cerebral venous thrombosis should be considered as the mainstay of the treatment. Anticoagulation with heparin or low molecular weight heparinoids is  the most accepted treatment. In acute phase, medical   or surgical management to decrease intracranial pressure (ICP) is   also recommended. If the patient's clinical  condition aggravates despite adequate anticoagulation, thrombolysis  or mechanical thrombectomy can be an additive option.