Hepatoprotective Effect of Zizyphus vulgaris on Carbon Tetrachloride (CCl4) Induced Liver Damage in Rats as Animal Models
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.31661/gmj.v2i3.95Keywords:
Zizyphus vulgaris, Carbon tetra-chloride, hepatoprotective effect, ratAbstract
Background: Finding protective agents with fewer adverse effects against toxin-induced liver injuries, as a key detoxifier and excreter organ, have always been a concern for researchers. Carbon tetra-chloride (CCl4)-induced liver damage has been introduced as an experimental model of liver damage. This study aimed to investigate the protective effect of ethanolic extract of Zizyphus vulgaris (ZV) against hepatic injury induced by CCl4 in laboratory rats.
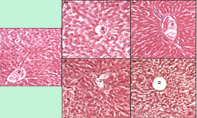
Methods: Fifty healthy male Wistar rats (200±20 g) were randomly divided into 5 groups (n=10) as following for a 45days study: Base, which received 1 cc/Kg olive oil intraperitoneally (IP) twice a week and 0.5cc distilled water orally; Control, which received 0.5 cc/kg olive oil+0.5 cc/Kg CCl4 IP+0.5cc distilled water orally; experimental groups, which received 0.5 cc/kg olive oil+0.5 cc/Kg CCl4 IP+0.5cc distilled water plus ZV extract in dosages of 200 mg/Kg (group E200),400 mg/Kg (group E400) and 600 mg/Kg (group E600) PO. Levels of aspartate-aminotransferase (AST), alanine-aminotransferase (ALT), alkaline-phosphatase (Alk-P), Albumin, total-protein, and bilirubin were measured as well as pathological assessment of the liver samples for scoring of portal inflammation and hepatocellular necrosis.
Result: Results of this study revealed that although there was a significant decrease in liver enzymes of the ZV treated groups (P<0.05) there were insignificant differences in protein and albumin concentrations between the 5 experimental groups. In addition, ZV treatment reduced hepatic necrosis and portal inflammation compared with the control group.
Conclusion: ZV showed hepatoprotective impact against CCl4-induced liver injury according to both serological and pathological investigations.