Investigating the Relationship between Hba1c Level and Dental Caries in Type 2 Diabetic Patients
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.31661/gmj.v13iSP1.3738Keywords:
Type 2 Diabetes; HbA1c; DMFT Index; Dental CariesAbstract
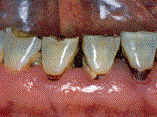
Background: Diabetes Mellitus is among the most frequent enduring metabolic disorders in the broad populace and leads to many complications, including tooth decay. In this study, the relationship between HbA1c level and dental caries has been investigated to be a step towards increasing awareness and improving the health status and quality of life of diabetics. Materials and Methods: This cross-sectional study was carried out on 20 type 2 diabetic who referred to dental clinic of shiraz university of medical sciences between 2022 and 2023 and were separated into two categories of managed diabetes (HbA1c under 7%) and uncontrolled (HbA1c above 7%). The desired data were obtained through a questionnaire containing demographic information, clinical examination (DMFT (Decayed, Missing, Filled Teeth) index), oral hygiene, and carbohydrate consumption. Results: The average DMFT index is greater in individuals with unmanaged diabetes compared to those with Controlled Diabetes, though not statistically significant (P=0.137). However, as BMI increases, so does the DMFT index (P=0.035). There is no notable correlation between HbA1c levels and dental caries (P=0.2). Oral hygiene practices did not significantly affect the DMFT index (P=0.943). Carbohydrate intake per day did not impact the DMFT (P=0.34). Higher education levels were associated with a decrease in DMFT, though not statistically significant (P=0.172). Conclusion: Considering the higher rate of dental caries in individuals with uncontrolled diabetes, it is necessary to inform these patients about more oral and dental hygiene and blood sugar control.
References
Alkahtani A, Grootveld M, Bhogadia M, Baysan A. Exploring Salivary Metabolic Alterations in Type 2 Diabetes: Implications for Dental Caries and Potential Influences of HbA1c and Vitamin D Levels. Metabolites. 2024;14(7):372.
https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo14070372
PMid:39057695 PMCid:PMC11279097
Hill-Briggs F, Adler NE, Berkowitz SA, Chin MH, Gary-Webb TL, Navas-Acien A et al. Social determinants of health and diabetes: a scientific review. Diabetes care. 2021;44(1):258.
https://doi.org/10.2337/dci20-0053
PMid:33139407 PMCid:PMC7783927
Banday MZ, Sameer AS, Nissar S. Pathophysiology of diabetes: An overview. Avicenna journal of medicine. 2020;10(04):174-88.
https://doi.org/10.4103/ajm.ajm_53_20
PMid:33437689 PMCid:PMC7791288
Cole JB, Florez JC. Genetics of diabetes mellitus and diabetes complications. Nature reviews nephrology. 2020;16(7):377-90.
https://doi.org/10.1038/s41581-020-0278-5
PMid:32398868 PMCid:PMC9639302
Klein S, Gastaldelli A, Yki-Järvinen H, Scherer PE. Why does obesity cause diabetes? Cell metabolism. 2022;34(1):11-20.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmet.2021.12.012
PMid:34986330 PMCid:PMC8740746
Galicia-Garcia U, Benito-Vicente A, Jebari S, Larrea-Sebal A, Siddiqi H, Uribe KB et al. Pathophysiology of type 2 diabetes mellitus. International journal of molecular sciences. 2020;21(17):6275.
https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21176275
PMid:32872570 PMCid:PMC7503727
Wu C-z, Yuan Y-h, Liu H-h, Li S-s, Zhang B-w, Chen W et al. Epidemiologic relationship between periodontitis and type 2 diabetes mellitus. BMC Oral Health. 2020;20:1-15.
https://doi.org/10.1186/s12903-020-01180-w
PMid:32652980 PMCid:PMC7353775
Agho ET, Owotade FJ, Kolawole BA, Oyetola EO, Adedeji TA. Salivary inflammatory biomarkers and glycated haemoglobin among patients with type 2 diabetic mellitus. BMC Oral Health. 2021;21:1-8.
https://doi.org/10.1186/s12903-021-01453-y
PMid:33676486 PMCid:PMC8095344
Isola G, Matarese G, Ramaglia L, Pedullà E, Rapisarda E, Iorio-Siciliano V. Association between periodontitis and glycosylated haemoglobin before diabetes onset: A cross-sectional study. Clinical oral investigations. 2020;24:2799-808.
https://doi.org/10.1007/s00784-019-03143-0
PMid:31776665
Ahmadinia AR, Rahebi D, Mohammadi M, Ghelichi-Ghojogh M, Jafari A, Esmaielzadeh F, Rajabi A. Association between type 2 diabetes (T2D) and tooth loss: a systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC endocrine disorders. 2022;22(1):100.
https://doi.org/10.1186/s12902-022-01012-8
PMid:35418054 PMCid:PMC9006550
Rapone B, Ferrara E, Corsalini M, Qorri E, Converti I, Lorusso F et al. Inflammatory status and glycemic control level of patients with type 2 diabetes and periodontitis: a randomized clinical trial. International journal of environmental research and public health. 2021;18(6):3018.
https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18063018
PMid:33804123 PMCid:PMC7998112
Chen Y-f, Zhan Q, Wu C-z, Yuan Y-h, Chen W, Yu F-y et al. Baseline HbA1c level influences the effect of periodontal therapy on glycemic control in people with type 2 diabetes and periodontitis: a systematic review on randomized controlled trails. Diabetes Therapy. 2021;12:1249-78.
https://doi.org/10.1007/s13300-021-01000-6
PMid:33481189 PMCid:PMC8099950
Aziz HK. The relationship between the dental caries and the blood glucose level among type II non insulin dependent diabetic patients. J Bagh Coll Dent. 2012;24(sp1):108-14.
Collin H-L, Uusitupa M, Niskanen L, Koivisto A-M, Markkanen H, Meurman JH. Caries in patients with non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Oral Surgery, Oral Medicine, Oral Pathology, Oral Radiology, and Endodontology. 1998;85(6):680-5.
https://doi.org/10.1016/S1079-2104(98)90035-X
PMid:9638701
Behbahani LR, Yasin A-E. Determining the DMFT index and its correlation with the Blood Sugar and HbA1c levels in type II diabetic patients in Ahvaz at 2016-2017. Int J Curr Res Chem Pharm Sci. 2017;4(2):19-24.
https://doi.org/10.22192/ijcrcps.2017.04.02.005
Yonekura S, Usui M, Murano S. Association between numbers of decayed teeth and HbA1c in Japanese patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Upsala journal of medical sciences. 2017;122(2):108-13.
https://doi.org/10.1080/03009734.2017.1285838
PMid:28276781 PMCid:PMC5441370
Majbauddin A, Tanimura C, Aoto H, Otani S, Parrenas MC, Kobayashi N et al. Association between dental caries indicators and serum glycated hemoglobin-levels among patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Journal of oral science. 2019;61(2):335-42.
https://doi.org/10.2334/josnusd.18-0156
PMid:31217384
Farahat F, Daneshkazemi A, Amiri M, Ebrahimpoor Aghdari A. Evaluation of DMFT index in type II diabetic patients and its correlation with HbA1c in Yazd city in 2013. Tolooebehdasht. 2016;15(1):150-61.
Jawed M, Khan RN, Shahid SM, Azhar A. Protective effects of salivary factors in dental caries in diabetic patients of Pakistan. Journal of Diabetes Research. 2012;2012(1):947304.
https://doi.org/10.1155/2012/947304
PMid:22778718 PMCid:PMC3388590
Stojanović N, Krunić J, Cicmil S, Vukotić O. Oral health status in patients with diabetes mellitus type 2 in relation to metabolic control of the disease. Srpski arhiv za celokupno lekarstvo. 2010;138(7-8):420-4.
https://doi.org/10.2298/SARH1008420S
PMid:20842885
Vivek B, Ramesh KS, Gautami PS, Sruthima GN, Dwarakanath C, Anudeep M. Effect of periodontal treatment on oral health-related quality of life-A randomised controlled trial. Journal of Taibah University Medical Sciences. 2021;16(6):856-63.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtumed.2021.07.002
PMid:34899130 PMCid:PMC8626792
Jouhar R, Ahmed MA, Khurshid Z, Bokhari SAH. Association of BMI, diet, physical activity, and oral hygiene practices with DMFT index of male dental students at King Faisal University, Al-Ahsa. Nutrients. 2021;13(1):224.
https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13010224
PMid:33466721 PMCid:PMC7828819
Ayan G, Dayı B. The Correlation Between Obesity and the Decayed, Missing, Filled Teeth (DMFT/dmft) Index. Türkiye Diyabet ve Obezite Dergisi. 2021;5(1):96-100.
https://doi.org/10.25048/tudod.818729
Mirzamohammadi H, Jafari A, Rezaee R, Daraei H, Shahsawari S, Rezaei S, Ebrahimi R. Assessment of DMFT and its influencing factors in guidance school students in Pirnshahr city, Iran. Journal of Advances in Environmental Health Research. 2017;5(1):16-22.
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Galen Medical Journal

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.







